أستلة
الأسْتَلَة (Acetylation) في الكيمياء هي تفاعل كيميائي عضوي يتم فيه إضافة مجموعة أسيتيل إلى مركب كيميائي.[2] لتفاعل الأستلة أهمية في الاصطناع العضوي وفي الكيمياء الحيوية. يسمى الكاشف الكيميائي الذي يسهم في إضافة مجموعة الأسيتيل الوظيفية باسم العامل المؤستل.
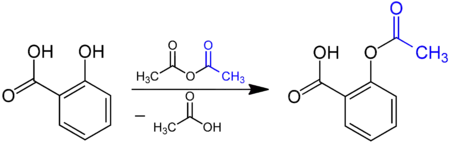
يعد تفاعل أستلة حمض الساليسيليك أثناء تحضير الأسبرين أحد أشهر الأمثلة على تفاعلات الأستلة.
الأستلة في الاصطناع العضوي
يستخدم تفاعل الأستلة في الاصطناع العضوي من أجل إضافة مجموعة الأسيتيل إلى المركبات العضوية، حيث أن تلك المجموعة تخدم كمجموعة حماية. عادة ما يستخدم أنهيدريد الأسيتيك كعامل مؤستل، حيث يعطي مردود جيد عند درجة حرارة الغرفة.[3][4]
كما يمكن أن يستخدم كلوريد الأسيتيل أيضاً كعامل مؤستل.[5][6]
الأستلة في الكيمياء الحيوية
يعد تفاعل الأستلة من تفاعلات التحويرات المهمة للبروتينات في الخلية، وقد أثبتت دراسات تحليل بنية البروتينات وجود الآلاف من البروتينات المؤستلة في الثدييات.[7][8][9]
مراجع
- Axel Kleemann, Jürgen Engel, Bernd Kutscher und Dieter Reichert: Pharmaceutical Substances, Thieme-Verlag Stuttgart, 5. Auflage (2009), S. 16−17, (ردمك 978-3-13-558405-8).
- Otto-Albrecht Neumüller (Herausgeber): Römpps Chemie Lexikon, Frank'sche Verlagshandlung, Stuttgart, 1983, 8. Auflage, S. 47, ISBN 3-440-04513-7.(بالألمانية)
- H. Büchi, H.G. Khorana: CV. Total synthesis of the structural gene for an alanine transfer ribonucleic acid from yeast. Chemical synthesis of an icosadeoxyribonucleotide corresponding to the nucleotide sequence 31 to 50. In: Journal of Molecular Biology. 72, 1972, S. 251–288, doi:10.1016/0022-2836(72)90148-9.
- R. I. ZHDANOV, S. M. ZHENODAROVA: Chemical Methods of Oligonucleotide Synthesis. In: Synthesis. 1975, 1975, S. 222–245, doi:10.1055/s-1975-23714.
- Gilbert Stork, Takashi Takahashi, Isao Kawamoto, Toshio Suzuki: Total synthesis of prostaglandin F2.alpha. by chirality transfer from D-glucose. In: Journal of the American Chemical Society. 100, 1978, S. 8272–8273, doi:10.1021/ja00494a045.
- Alan C. Spivey, Stellios Arseniyadis: Nucleophilic Catalysis by 4-(Dialkylamino)pyridines Revisited?The Search for Optimal Reactivity and Selectivity. In: Angewandte Chemie International Edition. 43, 2004, S. 5436–5441, doi:10.1002/anie.200460373.
- Choudhary C, Kumar C, Gnad F, Nielsen ML, Rehman M, Walther TC, Olsen JV, Mann M (2009). "Lysine acetylation targets protein complexes and co-regulates major cellular functions". Science. 325 (5942): 834–840. Bibcode:2009Sci...325..834C. doi:10.1126/science.1175371. PMID 19608861. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - Fritz KS, Galligan JJ, Hirschey MD, Verdin E, Petersen DR (2012). "Mitochondrial acetylome analysis in a mouse model of alcohol-induced liver injury utilizing SIRT3 knockout mice". J. Proteome Res. 11 (3): 1633–1643. doi:10.1021/pr2008384. PMC 3324946. PMID 22309199. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - Brook, Tom. "Protein Acetylation: Much More than Histone Acetylation". Cayman Chemical. مؤرشف من الأصل في 18 أكتوبر 2015. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة)
- بوابة علم الأحياء الخلوي والجزيئي
- بوابة الكيمياء
