ولبخية
الولبخية هي جنس من البكتيريا تصيب مفصليات الأرجل وبضمنها نسبة عالية من الحشرات بالإضافة لبعض الديدان الأسطوانية.
اضغط هنا للاطلاع على كيفية قراءة التصنيف Wolbachia | |
|---|---|
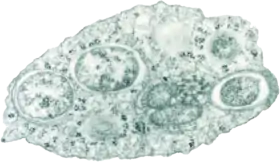 صورة مأخوذة بواسطة مجهر إلكتروني نافذ للولبخية داخل خلية مصابة بالعدوى. صاحب الصورة:المكتبة العامة للعلوم / Scott O'Neill | |
| المرتبة التصنيفية | جنس |
| التصنيف العلمي | |
| المملكة: | بكتيريا |
| الشعبة: | متقلبات |
| الطائفة: | متقلبات ألفا |
| الرتبة: | ريكتسيات |
| الفصيلة: | ريكتسية |
| الجنس: | ولبخية Wolbachia |
| الاسم العلمي | |
| Wolbachia | |
| الأنواع | |
| Wolbachia melophagi Wolbachia persica ولبخية | |
الأنواع
لا يمكن لأغلب أنواع الولبخية أن تعيش وتتكاثر خارج معيل حقيقي النواة لذلك لم تمنح اسما لاتينيا رسميا.
التسمية
أصل تسمية الولبخية يعود للعالم الأمريكي سيميون بورت ولباخ [الإنجليزية] الذي وصف الجنس أول مرة مع مارشال هرتج (Marshall Hertig) عام 1924 في الباعضة الناصبة (Culex pipiens). وقد قام مارشال هرتج لاحقا بوصف النوع بأنه ولبخية ناصبة (Wolbachia pipientis) رسميا عام 1936.[6]
المصادر
- Dumler JS, Barbet AF, Bekker CP, et al. (نوفمبر 2001). "Reorganization of genera in the families Rickettsiaceae and Anaplasmataceae in the order Rickettsiales: unification of some species of Ehrlichia with Anaplasma, Cowdria with Ehrlichia and Ehrlichia with Neorickettsia, descriptions of six new species combinations and designation of Ehrlichia equi and 'HGE agent' as subjective synonyms of Ehrlichia phagocytophila". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 51 (Pt 6): 2145–65. doi:10.1099/00207713-51-6-2145. PMID 11760958. مؤرشف من الأصل في 28 مارس 2013. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - Lo N, Paraskevopoulos C, Bourtzis K, et al. (مارس 2007). "Taxonomic status of the intracellular bacterium Wolbachia pipientis". Int. J. Syst. Evol. Microbiol. 57 (Pt 3): 654–7. doi:10.1099/ijs.0.64515-0. PMID 17329802. مؤرشف من الأصل في 11 أبريل 2016. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - Forsman M, Sandström G, Sjöstedt A (January 1994). "Analysis of 16S ribosomal DNA sequences of Francisella strains and utilization for determination of the phylogeny of the genus and for identification of strains by PCR". Int. J. Syst. Bacteriol. 44 (1): 38–46. doi:10.1099/00207713-44-1-38. PMID 8123561. مؤرشف من الأصل في 27 سبتمبر 2016. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة)صيانة CS1: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفون (link) - Noda H, Munderloh UG, Kurtti TJ (October 1997). "Endosymbionts of ticks and their relationship to Wolbachia spp. and tick-borne pathogens of humans and animals". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63 (10): 3926–32. PMC 168704. PMID 9327557. مؤرشف من الأصل في 30 نوفمبر 2019. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة)صيانة CS1: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفون (link) - Niebylski ML, Peacock MG, Fischer ER, Porcella SF, Schwan TG (October 1997). "Characterization of an endosymbiont infecting wood ticks, Dermacentor andersoni, as a member of the genus Francisella". Appl. Environ. Microbiol. 63 (10): 3933–40. PMC 168705. PMID 9327558. مؤرشف من الأصل في 30 نوفمبر 2019. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة)صيانة CS1: أسماء متعددة: قائمة المؤلفون (link) - Hertig, Marshall; Wolbach, S. Burt (1924). "Studies on Rickettsia-Like Micro-Organisms in Insects". Journal of Medical Research. 44 (3): 329–74. PMC 2041761. PMID 19972605. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة)
Wolbachia في المشاريع الشقيقة
 صور وملفات صوتية من كومنز
صور وملفات صوتية من كومنز أنواع من ويكي أنواع.
أنواع من ويكي أنواع.
- بوابة علم الأحياء الدقيقة
- بوابة علم الأحياء
This article is issued from Wikipedia. The text is licensed under Creative Commons - Attribution - Sharealike. Additional terms may apply for the media files.
