مانومتر
المانومتر أو مقياس الضغط أو ميزان الضغط جهاز يستعمل في قياس ضغط الماء، الغاز أو البخار.[1][2][3] وهناك عدة أنواع من مقاييس الضغط. يتكون أبسط نوع منها من أنبوب على شكل الحرف اللاتيني (U) بنهايتين مفتوحتين. ويحتوي الأنبوب على سائل يكون عادة الزئبق يملأ قاع الأنبوب، ويرتفع قليلاً داخل ذراعي الأنبوب. ويقوم الشخص المستخدِم لهذا الجهاز بتوصيل إحدى الذراعين بالغاز المراد قياس ضغطه بينما تظل الذراع الأخرى مفتوحة تجاه الغلاف الجوي. وبهذه الطريقة يتم تعريض السائل لضغط الغاز داخل إحدى الذراعين وإلى الضغط الجوي في الذراع الأخرى.
فإذا كان ضغط الغاز أكبر من الضغط الجوي يرتفع السائل داخل الذراع المعرضة للهواء، ويقيس الشخص الفرق بين الارتفاعين لإيجاد ضغط السائل. يساوي هذا الضغط ناتج ضرب الفرق بين الارتفاعين في الثقل النوعي للسائل. ويكون ضغط الغاز مساويًا لحاصل جمع ضغط السائل والضغط الجوي.
وفي بعض مقاييس الضغط يُفرَّغ الهواء من إحدى ذراعي الأنبوب وتغلق الذراع. ويساعد هذا في التخلص من الحاجة إلى التعديلات الناجمة عن تغيّرات الضغط الجوي. أما الفرق بين مستويات السائل في الذراعين فيبيّن ضغط الغاز. ويقاس ضغط الغاز بوحدات تقابل ارتفاع السائل. فمقياس الضغط المعروف بالبارومتر مثلاً، يقيس الضغط الجوي بالسنتمترات الزئبقية. وتعمل بعض مقاييس الضغط بطريقة ربط زمبرك إلى مؤشر يتحرك أمام مقياس مدرج يوضح قراءات الضغط المباشرة. ويستعمل الأطباء أحد مقاييس الضغط يعرف بمقياس ضغط الدم لقياس ضغط الدم.
الضغوط المتفاوتة، القياسية، والمطلقة
ان الضغط المطلق يساوي = ضغط الغاز + الضغط الجوي
الوحدات
قالب:Pressure Units
الضغط الديناميكي والثابت
تطبيقات
- مقياس الارتفاع
- مقياس ضغط جوي
- MAP sensor
- أنبوب بيتو
- مقياس ضغط الدم
الآلات
عمود السائل
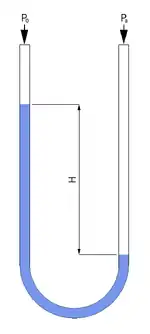
Types of fluid Manometers]</ref>
- Simple Manometer
- Micromanometer
- Differential manometer
- Inverted differential manometer

بوردون

التفاصيل الميكانيكية
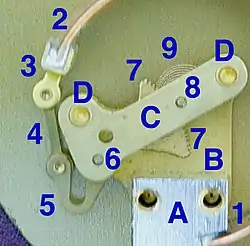
Stationary parts:
- A: Receiver block. This joins the inlet pipe to the fixed end of the Bourdon tube (1) and secures the chassis plate (B). The two holes receive screws that secure the case.
- B: Chassis plate. The face card is attached to this. It contains bearing holes for the axles.
- C: Secondary chassis plate. It supports the outer ends of the axles.
- D: Posts to join and space the two chassis plates.
Moving Parts:
- Stationary end of Bourdon tube. This communicates with the inlet pipe through the receiver block.
- Moving end of Bourdon tube. This end is sealed.
- Pivot and pivot pin.
- Link joining pivot pin to lever (5) with pins to allow joint rotation.
- Lever. This an extension of the sector gear (7).
- Sector gear axle pin.
- Sector gear.
- Indicator needle axle. This has a spur gear that engages the sector gear (7) and extends through the face to drive the indicator needle. Due to the short distance between the lever arm link boss and the pivot pin and the difference between the effective radius of the sector gear and that of the spur gear, any motion of the Bourdon tube is greatly amplified. A small motion of the tube results in a large motion of the indicator needle.
- Hair spring to preload the gear train to eliminate gear lash and تلاكؤ.
Diaphragm

Shape:
- Flat
- corrugated
- flattened tube
- capsule
أجهزة الضغط الاستشعار الالكترونية
- Piezoresistive Strain Gage
- Uses the piezoresistive effect of bonded or formed strain gauges to detect strain due to applied pressure.
- Capacitive
- Uses a diaphragm and pressure cavity to create a variable مكثف (كهرباء) to detect strain due to applied pressure.
- Magnetic
- Measures the displacement of a diaphragm by means of changes in محاثة تبادلية (reluctance), محول تفاضلي متغير خطي, تأثير هول, or by تيار دوامي (كهرومغناطيسية) principal.
- Piezoelectric
- Uses the كهرباء انضغاطية effect in certain materials such as quartz to measure the strain upon the sensing mechanism due to pressure.
- Optical
- Uses the physical change of an optical fiber to detect strain due applied pressure.
- Potentiometric
- Uses the motion of a wiper along a resistive mechanism to detect the strain caused by applied pressure.
- Resonant
- Uses the changes in رنين (فيزياء) in a sensing mechanism to measure stress, or changes in gas density, caused by applied pressure.
الكاثود الساخن

المعايرة
تتم بوضع أحد الطرفين عند مكان الغاز ثم النظر إلى المؤشر
History
القياسية الأوروبي (س)
- EN 472 : Pressure gauge - Vocabulary.
- EN 837-1 : Pressure gauges. Bourdon tube pressure gauges. Dimensions, metrology, requirements and testing.
- EN 837-2 : Pressure gauges. Selection and installation recommendations for pressure gauges.
- EN 837-3 : Pressure gauges. Diaphragm and capsule pressure gauges. Dimensions, metrology, requirements and testing..
انظر أيضا
- deadweight tester
وصلات خارجية
المصادر
- "معلومات عن مانومتر على موقع thes.bncf.firenze.sbn.it". thes.bncf.firenze.sbn.it. مؤرشف من الأصل في 12 ديسمبر 2019. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - "معلومات عن مانومتر على موقع zthiztegia.elhuyar.eus". zthiztegia.elhuyar.eus. مؤرشف من الأصل في 12 ديسمبر 2019. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة) - "معلومات عن مانومتر على موقع vocab.getty.edu". vocab.getty.edu. مؤرشف من الأصل في 16 أبريل 2020. الوسيط
|CitationClass=تم تجاهله (مساعدة)
- بوابة الفيزياء
